Geotechnical Engineering course Level 1
- Description
- Curriculum
- FAQ
- Reviews
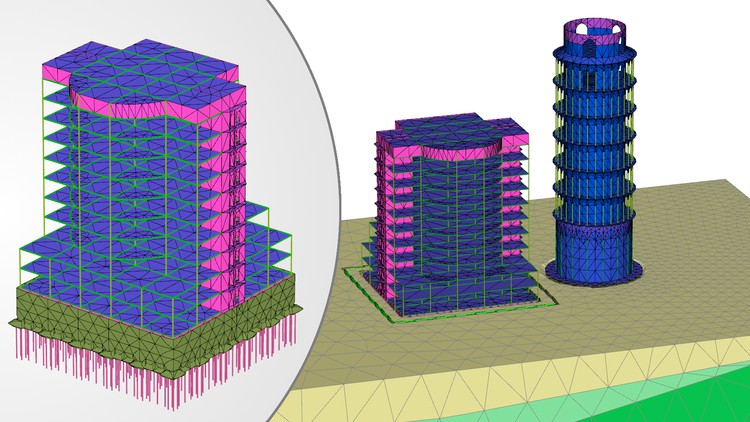
Geotechnical Engineering course
this course is for civil engineers, students, and structural engineers who interested in learning about geotechnical engineering
Level 1
Geotechnical Properties of Soil:
1- Geological Soil ( classification, types, description, properties, and physical relations ).
2- Water in soil ( subsurface water, flow of water, darcy’s low, coefficient of permeability, flow nets, seepage analysis, piping, filter design, total and effective stresses, earth dams).
3- Shear strength ( friction, cohesion, mohr circle, mohr-coulomb theory, shear parameters calculations, triaxial test, soil behavior under shear, sensitivity, and activity of clay, residual strength).
4- Stress analysis ( stress-strain relationships, stresses due to different loads, bulbs of pressure, shear stresses, contact pressure ).
5- Stability of slopes ( shear strength parameters, stability analysis of “infinite and finite slopes “, slopes design methods, slopes protection and treatment).
6- Earth pressure ( coefficients of earth pressure, methods of calculating earth pressure).
7- Compaction of soil.
8- Settlement in soil ( elastic settlement due to “concentrated load-area load-circular or irregularly shaped load – consolidation ).
9- Bearing capacity of the soil.
Level 2
Site Investigation, Subsurface
Exploration and Geotechnical Report:
1- General requirements.
2- Information required from site investigation.
3- Boreholes layout.
4- Exploration in soils and rocks.
5- Groundwater.
6- Geotechnical problems must be taken into consideration.
7- Field tests.
8- Laboratory tests on soils and rocks.
9- Data must be included in the soil report.
10- Prepare a geotechnical report.
11- Foundation properties of soil types.
12- Foundation properties of rock.
13- Important topics.
Level 3
Shallow Foundation Design:
1- Isolated footing.
2- Combined footing.
3- Strap-beam footing.
4- Wall footing.
5- Strip footing.
6- Project “ 5 stories building-foundation “.
7- Raft foundation.
8- Project “ 10 stories building-foundation”.
Level 4
Deep Foundations and Basement Design:
1- Piles.
2- Piled Raft.
3- Project “ 15 stories building-foundation”.
4- Pile cap.
5- Project “ bridge foundation ”.
6- Deep shaft foundations.
7- Buoyancy rafts and basements
8- Drag-down effects on deep foundations
9- Buoyancy raft foundation
10- Basement “box foundations”
11- Piled basements
12- Project “ 3 underground basements”
13- Geotechnical design report
14- Technical report “ case study -check on foundation report-”
Level 5
Retaining Structures And Deep Excavation:
1- Conditions of the adjacent properties.
2- Confirmation of the conditions of the site.
3- Design criteria.
4- Cantilever retaining walls.
5- Counterfort retaining walls.
6- Sheet pile retaining systems.
Steel sheet pile.
Secant piles.
Tangent piles.
Diaphragm walls.
7- Soldier piles.
8- Soil nails wall.
9- Full open cut.
10- Braced excavation.
11- Anchored excavation.
12- Strutting systems.
13- Top-down construction.
14- Stability analysis “ very important”
15- Excavation and protection of adjacent buildings.
Level 6
Design Of Dewatering Systems:
1- Methods of dewatering.
2- Open sumps
3- Deep wells
4- Well points
5- Confined aquifers
6- Unconfined aquifers
7- Pumping tests
8- Selection of dewatering method
9- Determination of hydraulic parameters
10- Determination of the capacity of wells
11- Estimation of the number of wells
12- Dewatering and ground settlement “very important”
Level 7
Foundations On Week Soils:
1- Collapsible soil
2- Definition and types of collapsible soil
3- Procedure for calculating collapse settlement
4- Foundation design in soils not susceptible to wetting
5- Foundation design in soils susceptible to wetting
6- Expansive soils
7- Nature of expansive soils
8- Swelling test
9- Foundation consideration
10- Construction on expansive soil
11- Sanitary landfills
12- General nature of sanitary landfills
13- Settlement of sanitary landfills
Level 8
Soil Improvement And Groundation Modification:
1- General principles of compaction
2- Empirical relationships for compaction
3- Field compaction
4- Vibroflotation
5- Blasting
6- Precompression
7- Sand drains
8- PVD
9- Lime stabilization
10- Cement stabilization
11- Fly-Ash stabilization
12- Stone columns
13- Sand compaction piles
14- Dynamic compaction
15- Jet grouting
16- Deep mixing
Level 9
Advanced Soil Mechanics And Foundation Design:
1- Soil dynamics
2- Design of machine foundations “ vibration – impact-earthquake”
3- Cofferdams “ components, dimensions, stability”
4- Geotextiles
5- MSE walls
6- Bridges foundations
7- Bridges on land
8- Bridges over water
9- Tunnels “ construction and design “
Softwares
plaxis 2d
plaxis 3d
geostudio
slide
midas gts nx
midas gen
دورة هندسة التربة و الأساسات
geotechnical engineering course
مجال الهندسة الجيوتقنية هو أحد أهم المجالات الهندسية يختص بالأعمال التالية :
1- أعمال إستكشاف الموقع و إجراء الإختبارات علي التربة و إعداد تقرير التربة و توصيات التأسيس
2- تصميم الأساسات السطحية و العميقة
3- تصميم الموني
4- تصميم الأنفاق
5- أعمال تحسين التربة
6- أعمال الحفر و السند
7- أعمال النزح
8- أعمال البنية التحتية
________________________________________________
تغطي هذه الدورة كافة هذه المواضيع من الناحية التنفيذية و التصميمية حيث ستشتمل علي دراسة طرق التنفيذ لمختلف الأعمال و كذلك طرق التصميم حسب الأكواد المختلفة ECP-AASHTO-FHWA-ACI
بالإضافة الي إستخدام مختلف البرامج الهندسية الجيوتقنية و الإنشائية في هذه الدورة مثل PLAXIS 2D – PLAXIS 3D – ALLPILE – SLIDE –WALLAP-MIDAS GTS NX- GEOSTUDEO- CSI SAP -CSI SAFE -CSI ETAPS
و يراعي أن هذه الدورة دورة ضخمة جدا نظرا لما تحتوية من مواضيع سيتم سردها علي المستوي العلمي و العملي و طرق التصميم اليدوي و استخدام البرامج المختلفة للوصول لفهم كامل لهذه المواضيع
تتكون هذه الدورة من 9 مستويات مختلفة تبدء من بداية تعريف التربة وصولا إلي الأعمال التصميمية المتقدمة
بحيث مع إنتهاء كل مستوي يصل المهندس لإتقان كامل و تام لمهارات المهندس الجيوتقني من الناحية الفنية و التصميمية و كذلك يتمكن المهندس الإنشائي من إستكمال الرؤية التصميمية بحيث يجمع ما بين النظرية الفلسفية للتصميم الإنشائي في إطار ضوابط الهندسة الجيوتقنية .
مهندس مصطفي مجدي
00201142649567
00201020155870
-
101- introduction to geotechnical course
-
202- soil types
-
303-0 seive analysis
-
403-1 correction of excel eq
-
504- hydrometer test
-
605- physical properties of soil
-
706- applications
-
807- calculation of cut and fill amounts
-
908- atterberg limits
-
1009- soil classification -1
-
1110- soil classification - 2 -ROCKS-
-
1200- intruduction to water in soil
-
1301- water in soil
-
1402- permeability
-
1503- permeability coefficient determination
-
1604- correction of constant head equation
-
1705- flow net and seepage analysis
-
1806- boiling condition-quick sand
-
1907- introduction to water flow analysis by softwares
-
2008- slide v-6.02 setup
-
2109- geostudio v 2018 setup
-
2210- plaxis 2D V20 - plaxis 3D V20 setup
-
2311- slide- cofferdam seepage model
-
2412- slide- earth dams seepage model
-
2513- slide- earth dams toe filter model
-
2614- slide- earth dams with core model
-
2715- important notes
-
2816- shear srength of soil
-
2917- shear teats (1)
-
3018- shear tests (2)
-
3119- shear tests (3)
-
3220- stresses in soil (1)
-
3321- stresses in soil (2)
-
3422- calculating stresses by newmark chart
-
3523- slope stability (1)
-
3624- slope stability (2)
-
3725- unconfined aquifer design (( deep well dewatering system ))
-
3826- Earth pressure (1)
-
3927- Earth pressure (2)
-
4028- earth pressure (3)
-
4129- earth pressure (4)
-
4230- soil compaction
-
4331- settlement in soil
-
4432- settlement in soil (2)
-
4533- settlement in soil (3)
-
4634- settlement in soil (4)
-
4735- soil bearing capacity (1)
-
4836- Important Note




Social Network